What is interwoven fabric?
Core Essence and Process Characteristics of Interwoven Fabrics
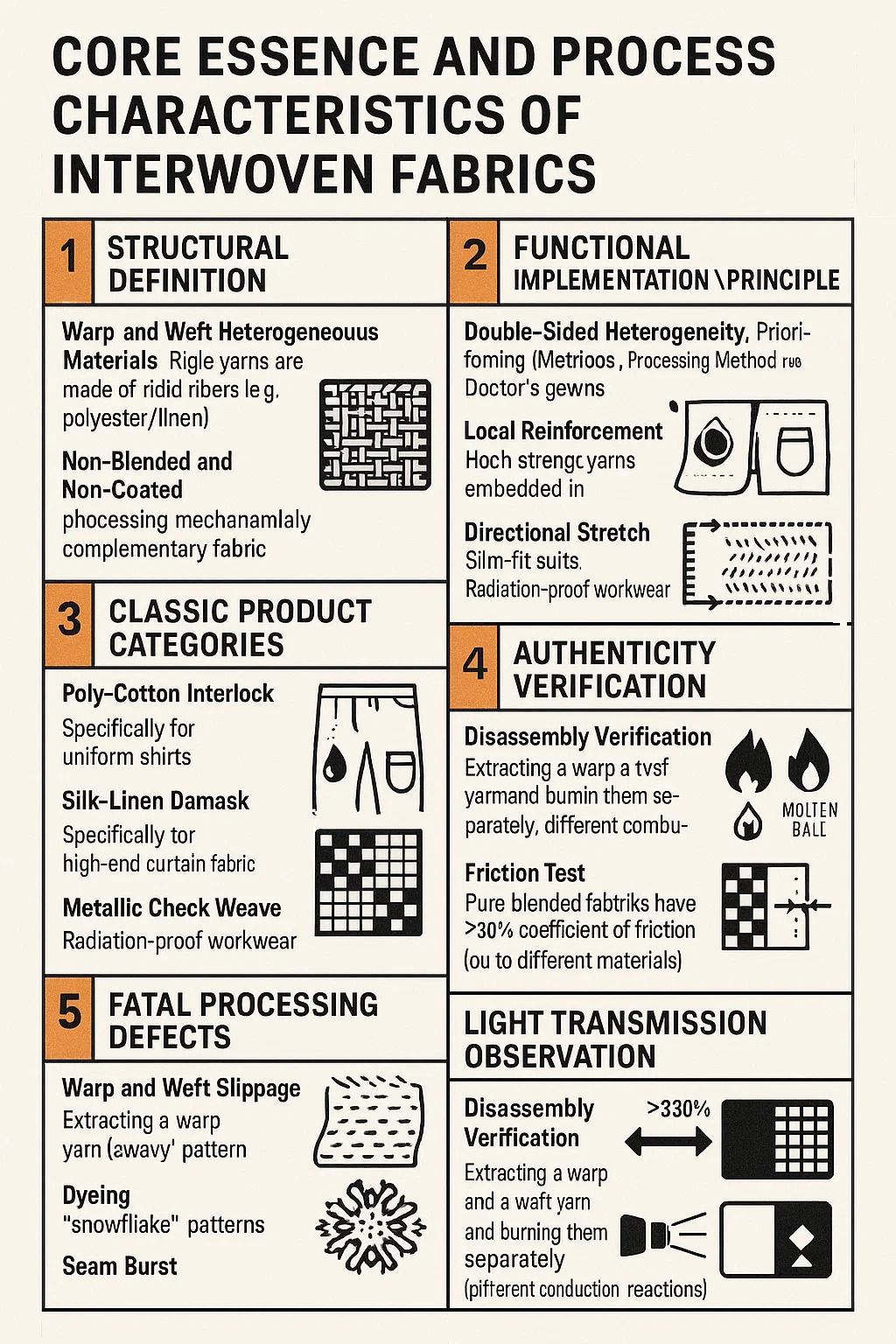
1. Structural Definition
Warp and Weft Heterogeneous Materials: The warp yarns are made of rigid fibers (e.g., polyester/linen), while the weft yarns are made of flexible fibers (e.g., cotton/viscose), creating a mechanically complementary fabric.
Non-Blended and Non-Coated: The yarns are interwoven in layers on the loom, without chemical fusion or surface treatment.
2. Functional Implementation Principle
| Performance Strength | Engineering Method | Industry Implementation |
| Dual-Surface Differentiation | Warp/Weft asymmetry: • Hydrophobic warp (e.g., polyester) • Hydrophilic weft (e.g., cotton) | Medical gowns: • Outer fluid-repellent • Inner moisture-wicking |
| Localized Reinforcement | Stress-point fiber grafting: • High-tensile yarns (e.g., nylon) • Zoned density weaving | Workwear reinforcement: • Kevlar®-core knee panels • Carbon-thread elbow patches |
| Directional Stretch | Controlled elasticity: • Rigid warp (e.g., linen) • Elastic weft (e.g., spandex) | Tailored garments: • Suit jackets (lateral stretch only) • Military uniform trim |
| Gradient Property Transition | Progressive fiber blending: • Warp: Wool Silk • Weft: Cotton Bamboo | Performance outerwear: • Ventilated cuffs → Insulated torso |
3. Classic Product Categories
Poly-Cotton Interlock: Polyester warp yarns provide the skeleton, cotton weft yarns provide a close-fitting, breathable feel—specifically for uniform shirts.
Silk-Linen Damask: Silk warp yarns create a lustrous sheen, linen weft yarns provide drape control—high-end curtain fabric.
Metallic Check Weave: Stainless steel warp yarns are conductive, while wool weft yarns provide warmth—radiation-proof workwear.
4. Fatal Processing Defects
Warp and Weft Slippage: Differential shrinkage rates of different materials → "wavy" patterns appear after washing (requires pre-shrinkage treatment).
Dyeing: Polyester-cotton interwoven fabrics dyed with cotton but not polyester → "snowflake" patterns appear (requires a double-dyeing process).
Seam Burst: Flexible weft yarns cut by the seams → thread breakage at the seam (requires ≥12 stitches within 3 cm).
5. Authenticity Verification
Disassembly Verification: Extract a warp yarn and a weft yarn and burn them separately—authentic interwoven fabrics will exhibit different combustion reactions (e.g., cotton weft ash/polyester warp molten balls).
Friction Test: Pure blended fabrics have the same coefficient of friction on both sides; interwoven fabrics exhibit a >30% difference (due to different materials).
Light Transmission Observation: Interwoven fabrics exhibit a regular grid pattern when light is transmitted (blended fabrics exhibit a cloud-like pattern).



 English
English 

 PREV
PREV








